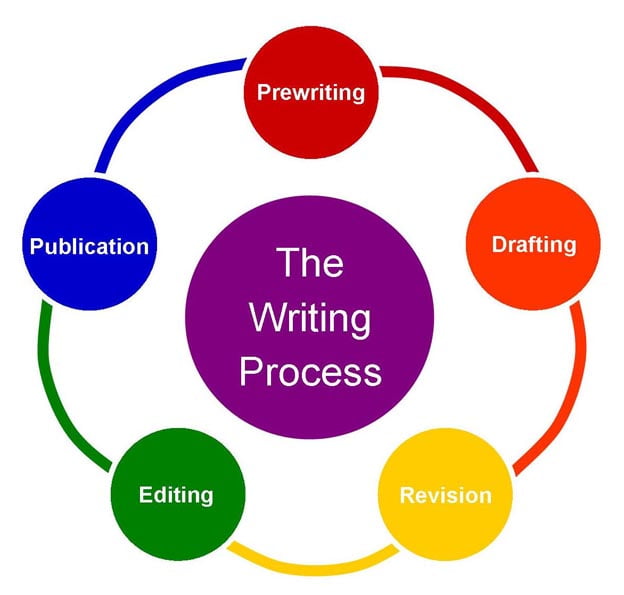
A simple, lucid writing style is often the product of long years of practice in using the language of various kinds in the written context. The writing process involves a series of stages. A written text requires planning, drafting, revising, editing and proofreading. These crucial phases in the writing process can be divided into four essential steps.
- Pre-writing (Planning)
- Writing
- Revision
- Editing and Proofreading
Step 1: Planning
This is the first stage, the ‘pre-writing stage’, comprising everything you do before writing a draft. It includes deciding the topic, defining the purpose of writing, brainstorming, researching and collecting data and outlining the text to be written.
Deciding on the Topic
It is always easier to write on a subject you are familiar with, which information is readily available, or which is practically possible to work on. In writing a term paper or an assignment, however, you can challenge yourself more by taking on a topic involving greater preparation and higher presentation skills.
Defining the Purpose
Once you decide on the topic, you need to ask yourself a few questions to get a better insight into the purpose and scope of your writing. The following questions will help you define the purpose and nature of your paper.
- What is my purpose in writing?
- What can I achieve with the document?
- Is it to entertain, convey a message or share an idea with someone?
- What do the readers know?
- And what do they need to know?
- Do the readers know about the information I am going to present?
- How can I establish rapport with the audience?
- What strategies can I employ to influence the readers and persuade them to act on my suggested lines?
Collecting Information
This is the third phase in the pre-writing stage of writing. Good content is the essence of good writing. Therefore, collecting appropriate content is of utmost importance. Let us try to understand some of the methods and techniques commonly used by writers.
- Brainstorming: This technique generates multiple ideas, usually through intensive and freewheeling group discussions. The brainstorming session does not involve any analysis cr, criticism, or discussion of ideas.
- Using WH questions: These are question words we employ to get information in everyday situations. Using WH questions can also be a technique or method used to generate more ideas and to get a better picture of the topic.
- Clubbing or Clustering: Clustering helps you explore ideas as they occur. A cluster is a collection of similar objects. We use this technique to organise ideas that have some connection in a group.
- Mind mapping: Mind mapping is a powerful graphic technique to capture your thoughts. Along with brainstorming, it is a crucial phase in certain kinds of analytical writing. It is used to visualise structure and classify ideas as a diagram.
- Research: Effective research lays the foundation for a good piece of writing. Once you have put the main ideas into your written text, you may need more detailed and authentic information to expand your arguments and develop fresh ideas.
- Note-making: It is an essential tool when you attempt any writing. Note-making is preparing our brief notes for a writing task based on the notes we have already qualified from a book or a lecture we have listened to. Note-taking helps us form our understanding of the topic we are trying to learn or write about.
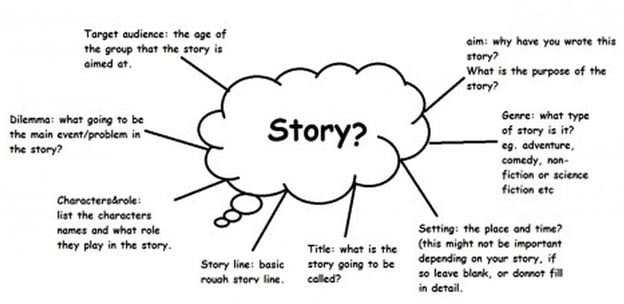
Structuring and Organising Ideas
The next step is to organise the ideas and content you have collected from your plan. You classify and categorise the information gathered through brainstorming, googling, reading and other methods.
Creating an Outline
The next stage is to create an outline. The purpose of an outline is to help you logically organise your thoughts and ideas by arranging them formally.
Step 2: Preparing the First Draft
At this stage, the focus should be more on the content than the language used. The outline you have developed and the organisation of the ideas may be tailored to suit the requirements of the different forms of writing.
Step 3: Revising the Text and Preparing the Final Draft
Revision is the key to writing effective documents. It is a critical path in the writing process. At the same time, revising, bear in mind the following suggestions.
- Avoid long sentences; make them simple and clear.
- Refine your prose, making each sentence as relevant as possible.
- Look for repetition of ideas. Use synonyms to avoid repetition of words.
- Aim for a reader-centred document.
- While revising, it is essential to review the text for coherence, cohesion and conciseness. They constitute the three ‘C’s in writing.
Coherence is the arrangement of ideas so that there is a smooth flow from the beginning to the end. Cohesion is related to the appropriate use of language in terms of grammar and vocabulary to ensure connections between sentences and paragraphs. Concise writing aims to be precise. Choosing specific, strong words is a big step towards effective writing.
Step 4: Editing and Proofreading
Editing refers to preparing a text for publication by correcting, revising or adapting the material. In the academic context, it refers to the final complete check regarding grammar and usage. Uniformity in style and formatting is also checked in the process. Careful editing makes your written text error-free and polished.
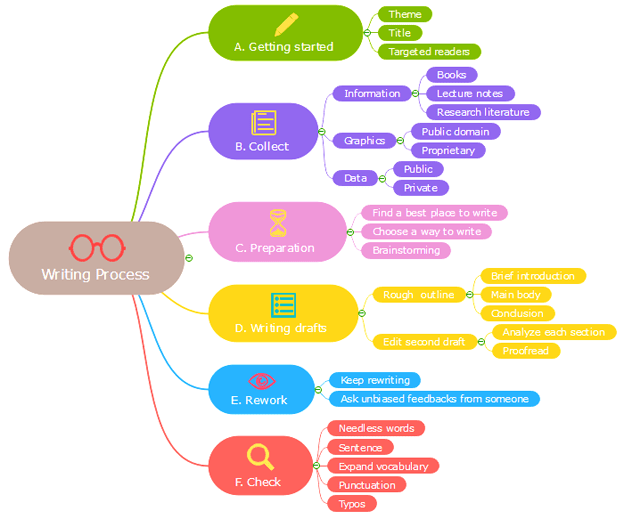
Using Computers
It is convenient to use computers at all the stages of writing, from preparing the draft to creating the final version. The following guidelines will help you design the text to make it readable and appealing to the readers.
- Times New Roman font is often preferred for formal documents, though you can use any font except very decorative or cursive ones. Verdana and Arial are other popular fonts used in formal documents. If the font used is Times New Roman, it is good to use font sizes 12, 12.5 or 13.
- In the ‘page settings’ option, ensure you have chosen A4 and provided margins of about 1 inch on all sides. The space between paragraphs could be 6 points, and the line spacing should ideally be double.
- In the ‘set language’ option, enable English(UK). In India, we usually follow the British spelling and grammar systems. Enable the check spelling as you type option.
- When you need to indent a line, always use the TAB key. Similarly, press the TAB key once when you want to insert the first line of a paragraph.
The points discussed are not specific to any writing, and all the steps will not be needed for all types of writing. But when you attempt academic or creative writing, like writing an essay or a story, it is desirable to plan well. With practice, you will gain more confidence with these stages, and writing will no longer be a ‘task’.